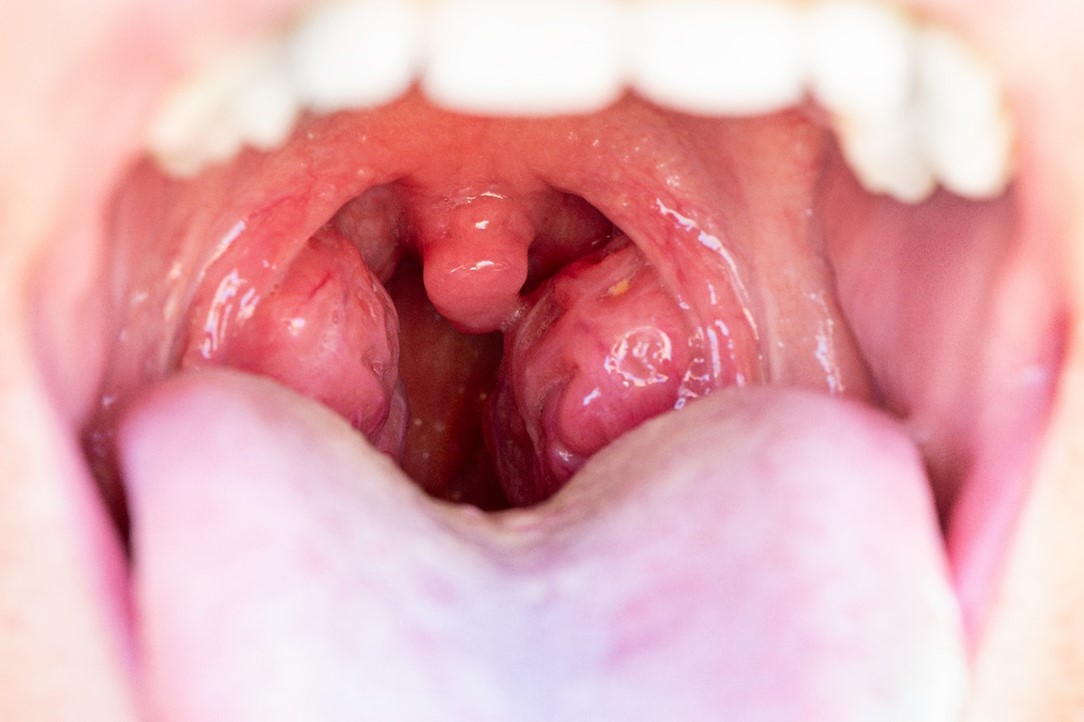
Tonsillitis is an infection that targets the tonsils, two lumps of tissue at the back of your throat.
These glands play a crucial role in immune defense, trapping germs that enter the airways and producing antibodies.
Tonsillitis can be acute, recurrent, or chronic, with acute episodes lasting up to two weeks and chronic conditions presenting long-term symptoms.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
The primary symptom of tonsillitis is swollen and inflamed tonsils, which make breathing through the mouth difficult.
Other common symptoms include
- Throat pain
- Fever
- Red tonsils with a white or yellow coating
- Painful blisters
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Ear pain
- Trouble swallowing
Causes and Diagnosis of Tonsillitis
Infections from either bacteria or viruses trigger tonsillitis.
Viral tonsillitis constitutes about 70% of cases and does not require antibiotics for treatment.
Bacterial tonsillitis, often caused by Streptococcus bacteria, necessitates antibiotics to avoid further health issues.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis usually starts with a physical examination followed by a throat swab to detect bacteria.
A complete blood count (CBC) may also assess the infection’s severity and nature.
Complications and Treatment
Viral tonsillitis often resolves independently, while bacterial tonsillitis must be treated with antibiotics to prevent serious complications such as peritonsillar abscesses and middle ear infections.
More severe risks include rheumatic fever and scarlet fever.
The effectiveness of treatment is typically noticeable within a few days; however, it’s critical to complete the entire course of antibiotics to clear the infection entirely.
Prevention and Recommendations
Preventing tonsillitis primarily involves:
- Maintaining excellent hygiene.
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Managing environmental factors like smog and humidity.
If tonsillitis symptoms, particularly fever or swelling, arise, immediate medical consultation is vital to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Enhanced Understanding and Additional Recommendations
Understanding the different strains of viruses and bacteria that can cause tonsillitis can further aid in its prevention and treatment.
Educating communities about the importance of vaccination, where applicable, such as the flu vaccine, can reduce the prevalence of viral tonsillitis.
Additionally, reinforcing the importance of not sharing personal items like utensils and toothbrushes can decrease the spread of infection.
It’s also beneficial to monitor air quality and reduce exposure to pollutants, as poor air quality can exacerbate throat irritations and contribute to the likelihood of tonsillitis.
Regularly cleaning shared surfaces and toys in schools and daycare environments can help reduce the spread of infections.
Act Fast: If you notice signs of tonsillitis, consult your doctor immediately to get the right treatment and prevent complications.